How to Read the Odometer on a Car Accurately: A Comprehensive Guide
The odometer is one of the most fundamental yet crucial components of a vehicle’s dashboard. It provides valuable information about the total distance a car has traveled since it left the factory. Whether you’re buying a used car, selling your vehicle, or simply keeping track of maintenance intervals, understanding how to read the odometer accurately is essential. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what an odometer is, the different types of odometers, common issues, and tips for ensuring accurate readings.
What is an Odometer?
An odometer is a device that measures the distance travelled by a vehicle. It is usually found on the vehicle’s dashboard and is displayed either in miles or kilometers, depending on the country and manufacturer. The word “odometer” comes from the Greek words “hodos,” meaning path or journey, and “metron,” meaning measure. Therefore, an odometer literally means “path measure.”

Types of Odometers
There are two primary types of odometers: mechanical and digital. Each type has its own method of calculating and displaying the distance travelled by the vehicle.
1. Mechanical Odometers
Mechanical odometers have been used for decades and are based on a series of gears and a flexible, rotating cable. This cable is connected to the vehicle’s transmission, which turns the gears inside the odometer. As the vehicle moves, the gears rotate, incrementing the numbers on the display to reflect the distance travelled.
-
- How It Works: The odometer cable is connected to a small gear inside the transmission. As the vehicle’s wheels turn, this gear rotates, turning the cable and, consequently, the gears in the odometer. The rotation of these gears moves the number dials on the odometer, recording the distance travelled.
- Accuracy: Mechanical odometers are generally accurate, but their accuracy can be affected by wear and tear on the gears or issues with the cable. Over time, the gears may become worn, leading to inaccurate readings.
2. Digital Odometers
Digital odometers are a more modern innovation, commonly found in vehicles manufactured from the late 1980s onwards. Instead of relying on mechanical gears, digital odometers use electronic sensors and microchips to calculate and display the distance travelled.
-
- How It Works: A sensor, usually located on the vehicle’s transmission or wheel hub, sends electronic signals to the vehicle’s onboard computer. The computer processes these signals to calculate the distance travelled and displays the result on a digital screen.
- Accuracy: Digital odometers are typically more accurate than mechanical ones because they are less prone to wear and tear. However, they can still be affected by electrical issues, software glitches, or tampering.
Common Odometer Issues
While odometers are generally reliable, they are not immune to problems. Here are some common issues that can affect the accuracy of an odometer reading:
1. Odometer Tampering
Odometer tampering, or “clocking,” is the illegal practice of rolling back an odometer to make it appear as though the vehicle has travelled fewer miles than it actually has. This is often done to increase the resale value of a used car. Both mechanical and digital odometers can be tampered with, although it is more challenging to tamper with a digital odometer due to the electronic systems involved.
-
- Signs of Tampering: If the numbers on a mechanical odometer are misaligned or if the wear on the vehicle does not match the mileage, these could be signs of tampering. For digital odometers, inconsistencies in service records or a dashboard warning light that stays on could indicate tampering.
2. Malfunctioning Odometers
Both mechanical and digital odometers can malfunction. For mechanical odometers, common issues include a broken cable, worn gears, or a stuck number dial. For digital odometers, problems could arise from faulty sensors, electrical issues, or software errors.
-
- Diagnosing the Issue: If your odometer is not working, it’s important to diagnose the issue promptly. For mechanical odometers, listen for unusual noises from the dashboard or transmission. For digital odometers, check for warning lights on the dashboard or unusual behaviour from the vehicle’s electronic systems.
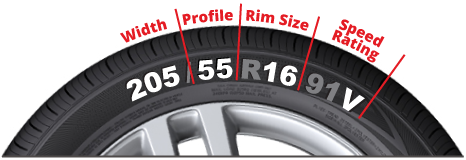
3. Incorrect Tyre Size
The accuracy of an odometer reading can also be affected by the size of the tires on the vehicle. The odometer is calibrated based on the original tire size specified by the manufacturer. If larger or smaller tires are installed, the odometer may record the distance travelled inaccurately.
-
- Impact on Reading: Larger tyres will cause the odometer to under-report the distance travelled, while smaller tires will cause it to over-report. This is because the odometer calculates distance based on the number of rotations of the tires, and different-sized tires rotate at different rates.
How to Ensure Accurate Odometer Readings
Accurate odometer readings are important for maintaining your vehicle and determining its value. Here are some tips to ensure that your odometer readings are as accurate as possible:
1. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring the accuracy of your odometer. For mechanical odometers, this means checking the odometer cable and gears for wear and tear. For digital odometers, it means keeping your vehicle’s electronic systems in good working order.
-
- Scheduled Inspections: Include odometer checks in your regular vehicle inspections. This will help you catch any issues early before they become major problems.
2. Use OEM Tyres
To maintain odometer accuracy, always use the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) tire size specified for your vehicle. If you need to change the tires, consult the vehicle’s manual or a professional to ensure that the new tires are the correct size.
-
- Tire Rotation and Pressure: Regularly rotating your tires and maintaining the correct tire pressure will also help ensure that your odometer reading remains accurate.
3. Check for Software Updates
For vehicles with digital odometers, manufacturers may release software updates that improve the accuracy of the vehicle’s electronic systems. Check with your vehicle’s manufacturer or dealer to see if there are any updates available for your vehicle.
-
- Updating Your Vehicle’s Software: Ensure that any software updates are installed promptly to prevent any issues that could affect the accuracy of your odometer reading.
4. Avoid Aftermarket Modifications
Aftermarket modifications, especially those that affect the vehicle’s transmission or electronic systems, can impact the accuracy of your odometer. If you are considering modifications, consult with a professional to understand how they might affect your vehicle’s odometer.
-
- Seek Professional Advice: If you have already made modifications, have a professional check the impact on your odometer to ensure continued accuracy.
Reading the Odometer: Step-by-Step Guide
Reading an odometer is straightforward, but accuracy is key, especially when you’re involved in transactions like selling or buying a used car.
Step 1: Locate the Odometer
The odometer is typically located on the vehicle’s dashboard, near the speedometer. For older vehicles, it might be a mechanical dial, while newer vehicles will have a digital display.
Step 2: Note the Number
Carefully note the number displayed on the odometer. This is the total distance the vehicle has traveled. If the odometer is mechanical, make sure the numbers are aligned correctly and not partially turned, as this can indicate a reading between two digits.
Step 3: Check for Additional Indicators
In some vehicles, the odometer may switch between total mileage and trip mileage. Ensure you’re reading the total mileage and not the trip meter, which records the distance traveled during a specific journey.
Step 4: Verify the Reading
If possible, compare the odometer reading with maintenance records or other documentation to ensure consistency. For vehicles with digital odometers, verify that the display is functioning correctly and shows no signs of malfunction.
Step 5: Record the Mileage
If you’re reading the odometer for a transaction or maintenance log, record the mileage accurately. Double-check the reading before writing it down to avoid errors.
Conclusion
Understanding how to read the odometer on a car accurately is vital for maintaining your vehicle, buying or selling a used car, and ensuring that your vehicle’s value is properly assessed. Whether your vehicle has a mechanical or digital odometer, being aware of potential issues and knowing how to address them will help you keep accurate track of your vehicle’s mileage.
Regular maintenance, using the correct tyre size, and avoiding unnecessary modifications are all key factors in ensuring the continued accuracy of your odometer. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently read and rely on your vehicle’s odometer, helping you make informed decisions about your car’s care and value.
Whether you’re a seasoned car owner or a first-time buyer, knowing how to accurately read and interpret your vehicle’s odometer is an essential skill that will serve you well throughout your driving experience.


Leave a Reply