What Is The Average Engine Hours For 100,000 Miles In The US?
Understanding the relationship between engine hours and mileage is crucial for vehicle owners, fleet managers, and automotive enthusiasts. This knowledge aids in assessing vehicle wear and tear, scheduling maintenance, and making informed purchasing decisions. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the concept of engine hours, explore the average engine hours corresponding to 100,000 miles in the U.S. and discuss factors influencing this metric. Additionally, we’ll touch upon tools like mileage blockers and odometer stoppers, examining their functions and implications.
What Are Engine Hours?
Engine hours refer to the total time an engine operates, regardless of whether the vehicle is moving or stationary. This metric is particularly significant for vehicles that experience substantial idling periods, such as commercial trucks, construction equipment, and emergency vehicles. Unlike mileage, which measures distance travelled, engine hours provide insight into the engine’s actual operational time, offering a more comprehensive view of its usage and potential wear.
Calculating Average Engine Hours for 100,000 Miles
Engine hours refer to the total time an engine operates, regardless of whether the vehicle is moving or stationary. This metric is particularly significant for vehicles that experience substantial idling periods, such as commercial trucks, construction equipment, and emergency vehicles. Unlike mileage, which measures distance traveled, engine hours provide insight into the engine’s actual operational time, offering a more comprehensive view of its usage and potential wear.
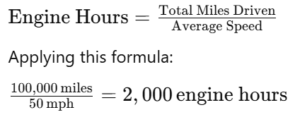
Therefore, at an average speed of 50 mph, a vehicle would accumulate approximately 2,000 engine hours over 100,000 miles. However, this is a simplified calculation. Real-world driving often involves varying speeds and idling periods, which can significantly affect engine hours.

Industry Insights and Variations In To Average Engine Hours
Industry standards suggest that average speeds for many vehicles range between 30 to 35 mph when accounting for idling and varying driving conditions. Using an average speed of 30 mph, the engine hours for 100,000 miles would be:
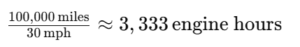
This indicates that vehicles with substantial idling or frequent stop-and-go traffic can accumulate more engine hours over the same mileage. For example, fleet vehicles or those used in urban settings may exhibit higher engine hours due to prolonged idling.
Discussions among vehicle owners further illustrate this variation. In a forum thread, a user inquired about engine hours for a GMC Sierra with 78,000 miles and 2,858 engine hours, questioning if this was excessive. Responses varied, with some noting that their vehicles had higher engine hours for similar mileage, while others reported lower figures, highlighting the influence of usage patterns and driving conditions
Factors Influencing Engine Hours
Several factors can affect the relationship between mileage and engine hours:
- Driving Habits: Frequent idling, aggressive driving, and rapid acceleration can increase engine hours and wear.
- Vehicle Type and Use: Commercial vehicles or those used in urban environments may experience more idling, leading to higher engine hours.
- Maintenance Practices: Regular maintenance, such as timely oil changes and engine checks, can mitigate wear associated with higher engine hours.
- Load and Terrain: Carrying heavy loads or driving in challenging terrains can increase engine strain, affecting the accumulation of engine hours.
The Role of Mileage Blockers and Odometer Stoppers
Mileage blockers, or sometimes known as odometer stoppers or mileage stoppers, are devices designed to pause the recording of mileage on a vehicle’s odometer. These tools are often marketed for testing or off-road purposes, allowing users to prevent mileage accumulation during specific scenarios.
For instance, Autotech UK offers a mileage blocker that stops the recording of mileage from all control units, ensuring that the filtered data remains untraceable even with diagnostic testers.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
While mileage blockers can serve many legitimate purposes, such as testing vehicle performance in controlled environments, their use on public roads is illegal in many jurisdictions. Altering or halting the recording of mileage with the intent to deceive potential buyers or misrepresent a vehicle’s usage is considered fraudulent and can lead to significant legal consequences.
It’s essential for vehicle owners and buyers to be aware of the potential for odometer tampering. Reports have highlighted the prevalence of odometer fraud, with some vehicles having their mileage rolled back to increase resale value. For example, in 2024, it was reported that over 2 million vehicles had their odometers tampered with, leading to consumers paying thousands of dollars more than the vehicles’ actual worth.
Best Practices for Vehicle Owners and Buyers
To ensure transparency and maintain vehicle integrity:
- Regular Maintenance: Adhere to recommended service schedules and keep detailed records of all maintenance activities.
- Monitor Engine Hours and Mileage: Regularly check both metrics to assess vehicle usage accurately.
- Be Cautious with Aftermarket Devices: Understand the legal implications of installing devices like mileage blockers and ensure they are used appropriately.
- Verify Vehicle History: When available confirm the service history of the vehicle with the service receipts/stamps in the service booklet to verify they are true.


Leave a Reply